
Research
Accurate and Reliable Solutions for the Animal Research Lab
During the early 2000s, our company operated under the previous name of Hamilton Thorne Biosciences and has since maintained strong ties in the animal research industry. We offer a full range of solutions to support clinical research, stem cell research, inner cell mass isolation, and other various developmental biology protocols.
Our research lasers have been used worldwide in a variety of applications including cellular injury and regeneration studies, fertilization of genetically modified lines, and laser-targeted cell ablation.
Our semen analyzers have been used in countless research applications in the developmental biology field and toxicology, pharmaceutical fields.
Your work is important to us. We understand the need for accuracy in quantitative studies and the need for repeatable results. Simplify your day-to-day operations and maximize your research potential!
Toxicology
Reproductive toxicology testing for a variety of substances, such as pharmaceuticals and chemicals, is necessary to verify there are no harmful effects on reproductive organs. We understand the critical role that you play to ensure a pathway of safety before medicinal drugs enter the clinical market. The TOX IVOS II semen analyzer helps identify if and how a drug or agent has some kind of impact on reproductive development or function during drug safety assessments and DART studies performed by Pharmaceutical companies and CROs (Contract Research Organizations).
- Our TOX IVOS has the capability to assess multiple animal species for drug development programs. The system has been used by world renowned companies such as Novartis, Charles River Laboratories, and Pfizer.
- Reproductive toxicology testing is also commonly performed on fish sperm to test for adverse effects of environmental contaminants. Our CEROS II semen analyzer is popular for fish studies with its option for a cooled stage to study cold water fish sperm.

Transgenics
Transgenics refers to the study of animals with an altered DNA structure for research purposes. This research includes various genetically modified animals but mostly focuses on rodent applications. Our lasers provide an efficient method for performing embryonic stem (ES) cell injection, 8-cell injection, and in vitro fertilization to preserve valuable rodent strains. The XYRCOS® or XYClone® laser can also be used as an easy alternative to single cell microinjection of lentiviruses into fertilized eggs.
In Transgenic repository labs, the IVOS and CEROS systems are used to help optimize the freezing of knock out and knock in transgenic and mutant mouse models. Our CASA and laser systems are also used in the ART and IVF procedures utilized to reconstitute these lines to live animal colonies for specific research testing around the globe.
“Laser-assisted ICSI using the XYClone® consistently achieved successful fertilization (up to 44% reported) utilizing thawed sperm that yielded 0% fertilization via conventional IVF. It has also shown to significantly increase the fertilization rate of known low fertilization sperm/oocyte combinations.”
Kathy Mohr, Facilities Director, Mutant Mouse Regional Resource Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
“Hamilton Thorne products provide a good method to make the reduction of animals real and supports the 3R’s guidelines in technical development.”
Ronald Naumann, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology

Stem Cell Research
Stem cell research refers to the study of using stem cells to replace damaged or diseased cells through regeneration medicinal procedures. Researchers also use stem cells to provide insight during the development of therapeutic drugs or to study disease.
- Our research lasers XYClone and XYRCOS have helped researchers study the transfer and development of pluripotent stem cells in rodent models. The Stiletto research laser has been used in a variety of applications including colony scoring and cell isolation.
- The Oosight Imaging system has been used to assess an oocyte’s biological structure during various research applications including the reprogramming of human somatic cells using human and animal oocytes (Chung et al., Cloning Stem Cells, 2009), somatic cell nuclear transfer, and genomic imprinting.
Applications in the Field

Semen Analysis
Our systems are designed to meet most regulatory requirements and contains additional algorithms to assess total sperm count from homogenized cauda epididymis under fluorescent illumination. Many medical research institutes and universities are using the HT CASA systems for these types of genetic specific research studies, as well as many others including environmental and behavioral studies. Medical research laboratories typically use our Animal Motility II software for sperm analysis of mice, hamsters, rabbit, non-human primates, and other laboratory animal species.
The TOX IVOS has been used in a variety of reproductive research studies including adverse effects on postnatal development in rat offspring (Li et al., Research Square, 2021), effects on sperm count, motility, and viability in rat (Bastaki et al., Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2019), effects of flower extract on oxidative balance of bovine spermatozoa (Benko et al., Contemporary Agriculture, 2019) and more!
“Because ‘sperm freezing’ is one of our backup technologies, the IVOS plays a big role in our lab. A standard sperm project is closed with two protocols: One is a fresh sperm measurement and the second is a controlled sample of thawed sperm.”
Ronald Naumann, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology
Cell Isolation and Colony Scoring for Stem Cell
Stem cell colonies may require cell isolation to sort individual cells or groups to perform research separately from the rest of the cell population. Our Stiletto® research laser can assist with colony scoring by applying the laser pulses in a crosshatch pattern within the selected areas. Cell colonies are quickly segmented for propagation. Users may designate the size of resulting sections. The video shows the scoring of a stem cell colony using the Stiletto.
Somatic Nuclear Cell Transfer (SCNT)
SCNT refers to the transfer of the nucleus of a somatic body cell to an enucleated egg for reproductive or therapeutic cloning purposes. Our Oosight Imaging System has helped with visualizing the oocyte’s meiotic spindle during transfer and with measuring oocyte viability. To assist with the ES-cell injection, our research lasers thin the egg’s zona pellucida prior to the donor cell insertion. Our products have been used in various SCNT procedures ranging from swine and bovine studies to exotic animals such as monkeys.
In 2018, a group of Chinese scientists at the Institute of Neuroscience in Shanghai were the first to successfully clone macaque monkeys using our Oosight Imaging system and our research laser.
(Liu Z, et al. Cloning of Macaque Monkeys by Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer. Cell (2018). 2018 Feb 8; 173: 1-7. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.020)
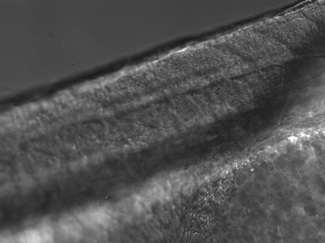
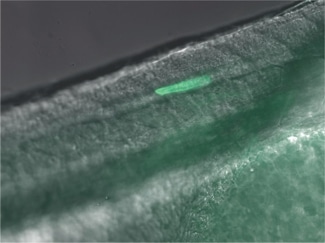
Heat-Induced Gene Activation
Heat-induced gene activation has been cited in numerous publications as an effective mechanism to study gene expression and gene therapy. This has both temporal and spatial control. The XYRCOS® and XYClone® laser offer a heating mechanism that is precisely controlled, as has been proven in assisted reproduction techniques. With the research laser’s Staccato multi-pulsing software feature, it is possible to sustain a precise, low-powered beam for long pulse duration.
In 2010 at the Marine Biology Labs in Woods Hole, MA; Jon Henry, one of the instructors at the Embryology course, performed a heat-induced gene activation on transgenic zebrafish. With the XYClone® laser and the Staccato multi-pulsing feature, it was possible to reproduce the results from the IR-LEGO system, as outlined in previous studies. The Staccato feature simulated the extended pulse duration in seconds as required.
